Jiva (consciousness) can be classified into two types:
(a) Liberated (Mukta)
(b) Sansāri (undergo cycle of birth and death): non-liberated souls. These can be classified into 563 divisions according to the Jain philosophy as follows:
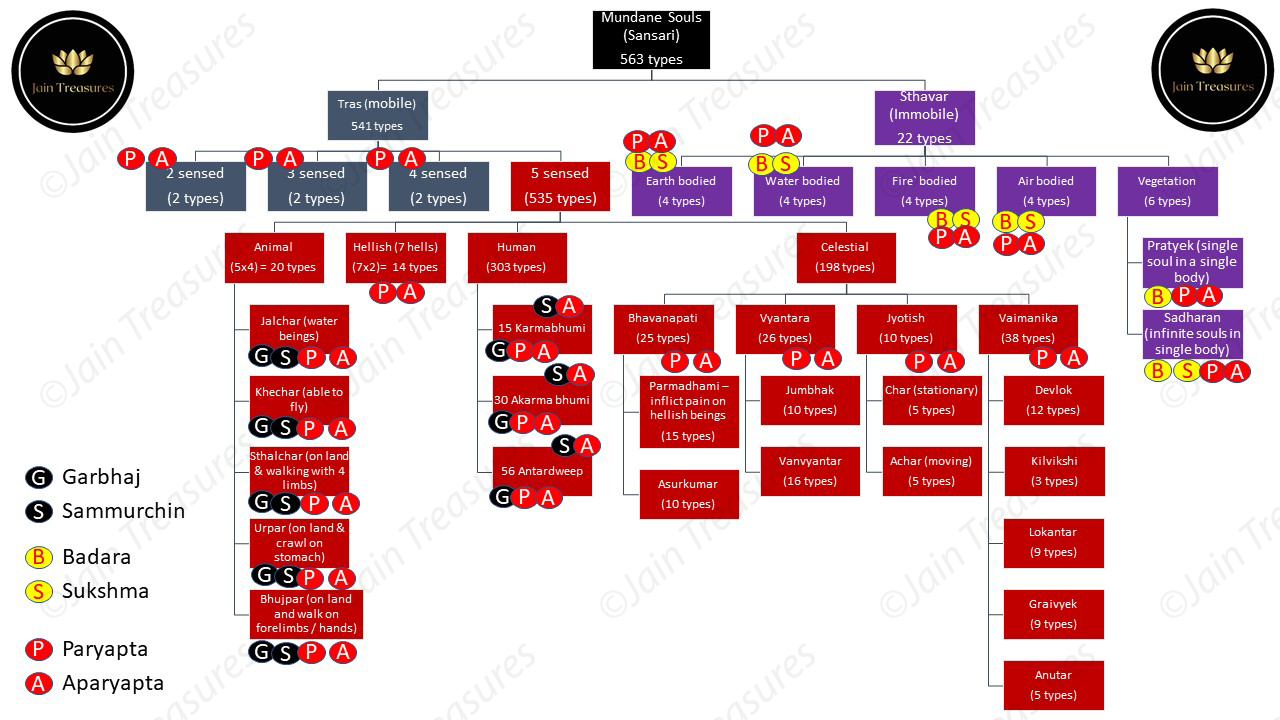
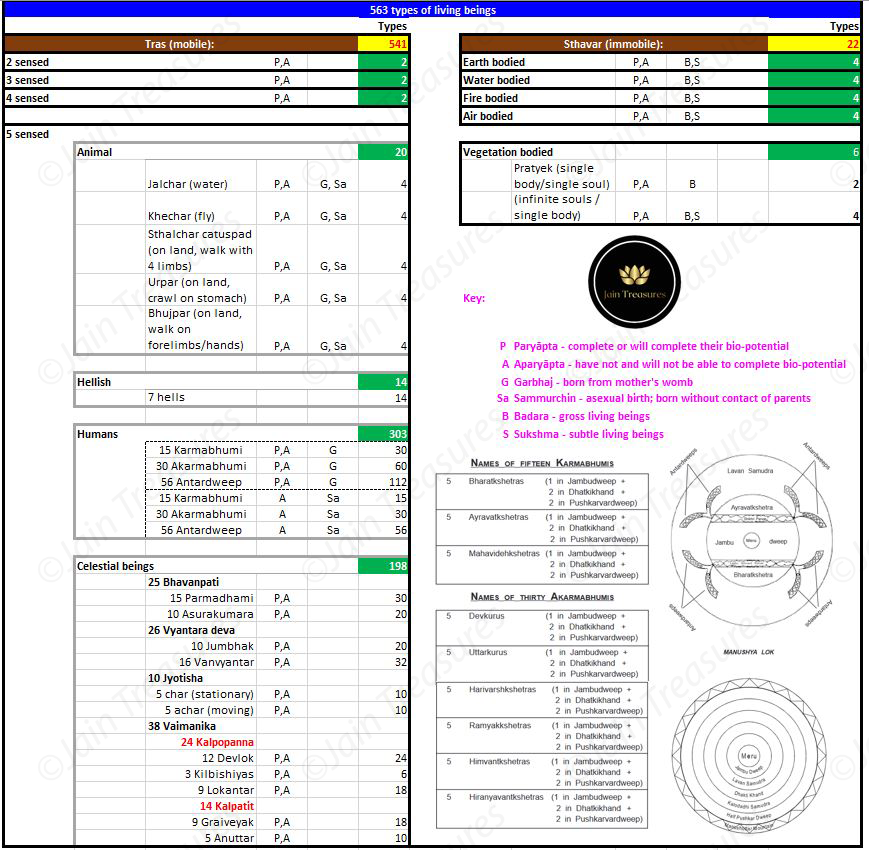
The meaning of the sub-divisions in the charts above are as follows:
(i) Paryāpta (P) and Aparyāpta (A): Click here for further details on these terms
(ii) Garbhaj (G) means born from mother’s womb with the contact of parents. It can be:
(a) born out of eggs e.g. birds
(b) born with a membraneous cover and joined to mother’s body e.g. humans
(c) born directly from the mother’s body without any membraneous cover e.g. lizards
(iii) Sammurchin means birth by assexual reproduction or spontaneous generation. It does not require parents. Jain tenet suggests that even humans can be born as sammurchin within excreta, cough, residual food, etc hence the attention to the code of conduct necessary in all human activities.
(iv) Bādara (B) means gross living beings
(v) Sukshma (S) means minute, fine, atomic or very subtle living beings
It is the permutation and combination of all the various sub-divisions which aggregates to 563 forms of living beings.
For example, in the animal kingdom Jalchar (water) beings can be Paryāpta (P) or Aparyāpta (A) and Garbhaj (G) or Sammurchin (Sa). Therefore, the total of 4 types is as follows:
- Paryāpta + Garbhaj
- Paryāpta + Sammurchin
- Aparyāpta + Garbhaj
- Aparyāpta + Sammurchin
References:
1. Jeev Vichar compiled by Acharya Hemchandrasuri (VS 2061)
2. Internet
I apologise and seek pardon for any unintentional errors in the above post.